Forest Service employee’s arrest after fire crosses onto private land sparks larger debate
Published 6:15 am Wednesday, October 26, 2022
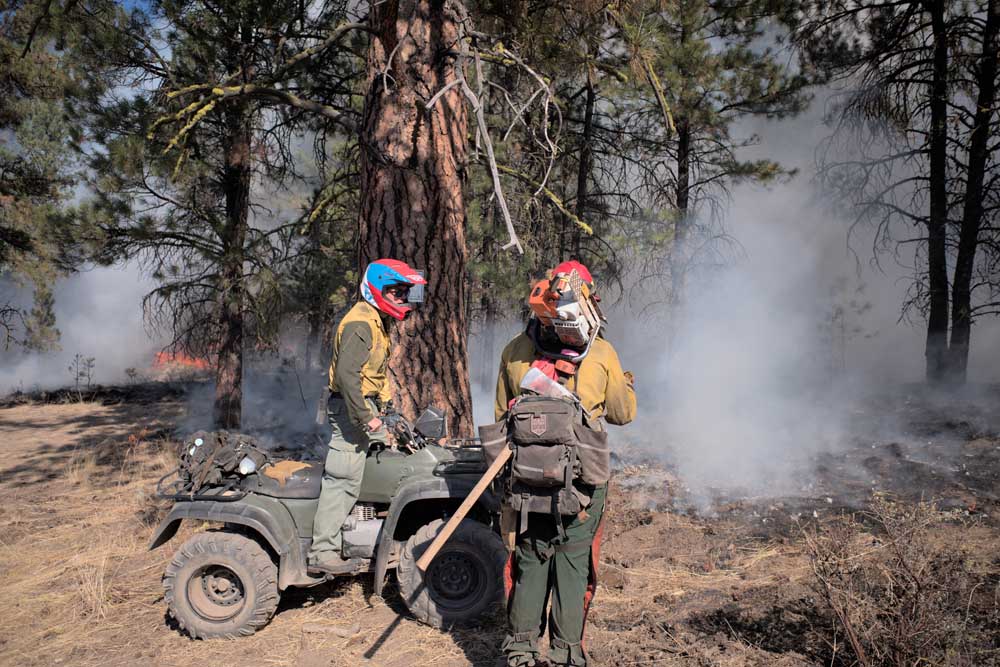

- A Forest Service crew member checks in with a contractor from Grayback Forestry as they monitor the fireline on the Starr 6 prescribed burn on Wednesday, Oct. 19, 2022.
When Rick Snodgrass approached Grant County Sheriff Todd McKinley, he thought the sheriff was there to help him.
Trending
According to Snodgrass, he’d called for law enforcement to help control aggressive traffic and to deal with harassment his crews had been receiving while implementing a prescribed burn on the Malheur National Forest in Bear Valley, about 7 miles north of Seneca.
That burn — called the Starr 6 — had since jumped the fireline, and now there was active fire on both sides of County Road 63, where Snodgrass and McKinley met: the prescribed burn operation on Malheur National Forest land to the north of the road — now flaring up in gusts of wind — and an uncontained slopover on private land to the south. The crews under Snodgrass’ direction were now attempting to quell one fire while holding the reins on another, with tempers, smoke, wind and now traffic adding to the dangers to his crew.
But instead of assistance, what Snodgrass got was arrested.
Trending
When the sheriff cuffed Snodgrass, it is thought to be the first time a U.S. Forest Service firefighter has been arrested in the course of performing their job.
Snodgrass, the “burn boss” on the day’s operation, was taken away from the scene and charged with reckless burning, a Class A misdemeanor that carries a maximum penalty of a year in jail and a $6,250 fine. Before it was contained, an hour after it kicked off, the spot fire burned an estimated 20 to 40 acres of private land owned by members of the Holliday family.
The arrest of Snodgrass on Wednesday, Oct. 19, has drawn national attention and has fanned the debate over Forest Service fire mitigation policies, especially as they pertain to intentional burns adjacent to private lands.
And in the aftermath of this burn, there are accusations on both sides of this contentious debate about which actions on that day deserve the blame. Critics of the Forest Service and the affected landowners feel the conditions on the day never should have allowed the burn to proceed. Others, including Forest Service personnel who planned and executed the burn, say that by arresting the burn boss at the moment of maximum danger, the planned operation and the safety of the crews were placed in jeopardy.
“Other individuals were able to pick up the slack, fortunately, that were well trained,” Snodgrass said. “He put not only my guys at risk out there, their safety, but he put that land at risk as well as, you know, all of Bear Valley.”
The buildup
In 2015 the Canyon Creek Fire, which started with lightning strikes on Malheur National Forest land and spread to private ground, ultimately burned over 110,000 acres and destroyed 43 structures in Grant County.
There is general agreement that a hundred years of fire suppression has led to forests that are overfilled with fuel, a situation made more dangerous by a prolonged drought. Part of Canyon Creek’s legacy is the strongly held and polarized views on how to best prevent catastrophic fires in the future.
Proponents of prescribed burning see the scorched canyons along US 395 as a reminder of the stakes, the need to create buffers, remove built-up fuels and restore forests to a pre-suppression state where they can better survive the inevitable blaze, while critics of federal land management and the Forest Service see a constant reminder of botched containment efforts and mismanaged public land that only fuel their distrust.
“Every individual has a different opinion and motivation,” said Craig Trulock, supervisor of the 1.7 million-acre Malheur National Forest. “You have people that are just anti-federal and don’t want any federal agency doing anything that could affect their lands. Others don’t like prescribed burning for various reasons, whether it’s risk or a sense that it doesn’t achieve what we should be doing out there because they want every log to go on a log truck. And then you have people that are saying, ‘When you burn, would you please burn my property as well?’”
According to Trulock, the burn had been going to plan. “We were within prescription on the burn,” Trulock said, noting he couldn’t say much more as the incident is now the subject of an active federal and local investigation.
The fire was the second day of prescribed burning in as many weeks. The burn area planned for Wednesday, Oct. 19, was 300 acres, including trees and meadowland within the Malheur National Forest in an operation involving federal, state and contract firefighting crews, according to information from the Forest Service.
This was among the first prescribed burns to be allowed after a new set of restrictions came into effect this year, following high-profile cases of prescribed burns getting out of control on federal land and causing massive damage, including the Calf Canyon/Hermit’s Peak blaze in New Mexico, which burned several hundred thousand acres and hundreds of structures this spring. After a 90-day pause on all prescribed burns, a revised set of restrictions was published.
As part of those new rules, before ignitions could begin in Bear Valley, a go/no-go checklist had to be completed on site.
This day’s final check represented the end of a multiyear process. That process involved an environmental analysis of the project area that included commercial logging, noncommercial thinning and burning treatments. The burn plan takes the form of a 100-plus-page document, updated year over year as the preparatory steps of thinning, fuel removal and tree grinding continued, all to get the area into ideal shape for a burn.
As part of the new rules, the final ignition authorization had to be signed by four people: the agency administrator, local unit line officer, burn boss, and fire management officer or duty officer. This process only authorizes ignitions for 24 hours, in effect giving all four officers veto power over the burn based on that day’s conditions.
On this day, all four individuals assessed the conditions, and all four signatures were affixed to the burn authorization, meaning ignitions could begin. One of those four signatures belonged to Rick Snodgrass.
Smoldering tensions
The ignition was delayed for about 45 minutes while crews did a grid search to ensure there were no cows in the burn area after hearing reports that the Hollidays still had some “stragglers” left on national forest land, a common occurrence as cows are seasonally moved off grazing allotments. The Windy Point Ranch allotment specified an Oct. 15 “off date,” but Chad Holliday explained that some fence that was burned the previous week, along with gates being left open by fire personnel, meant he couldn’t be sure the cattle were all out.
Initially, the burn went according to plan, with light winds of 0-3 mph and the heat of the fire drawing smoke up into a clean, bent column over the county road. The fire moved slowly across 50 acres over the course of five hours, with fire crews monitoring the progress of its leading front and continuing drip-torch ignitions.
Ignitions paused in the afternoon, to begin again a couple hours later. It was then that the wind picked up and a few trees in the interior of the already-burned area torched, sending up “duffers” with the smoke, up and over the road.
Members of the Holliday family, who own the Windy Point Ranch and other land adjacent to the burn area, were standing across the county road from the fire as an ember from the burn area touched town on their ranch, starting a new fire that soon began to spread.
“We were glad to see Oregon Department of Forestry and Grayback (contract crews) show up,” said Mandy Taylor, Chad Holliday’s sister.
ODF and Grayback Forestry crews were contracted to work alongside Forest Service employees throughout the day’s burn, but due to tensions between the landowners and the federal crews, they were eventually asked to take over mop-up after the flames of the spot fire were extinguished, according to Trulock, who said the move was meant to calm tensions on the scene.
Those kinds of tensions are not unusual.
“I think in a lot of parts of Oregon, it’s just a very real experience for federal employees to have a lot of hostility towards what they’re doing right now,” said Christopher Adlam, a regional fire specialist for Oregon State University’s Extension Service. “I’m not saying that people don’t also appreciate firefighters and thank firefighters. But it’s a pretty common thing in some parts of Oregon for federal employees to face hostility.”
Indeed, federal crews called the regional interagency dispatch center on both days of the burn to report verbal harassment, threats and aggressive driving through the smoke, and to request law enforcement assistance on the scene.
The Hollidays maintain they were welcoming and cooperative with federal crews, providing access to their land in order to contain the blaze. But as the fire spread and crews worked to contain it, the Hollidays called 911. They didn’t call to report the fire. They asked for the sheriff. “We knew that somebody was doing something wrong,” said Taylor.
Planning for contingencies
If you use the phrase “controlled burn” in the vicinity of firefighters operating a prescribed burn, you will be corrected.
This is fire. You don’t control it. The best you can plan for is to manage it and be prepared if the fire has other ideas.
Adlam points out that spillover fires like the one that happened in Bear Valley are rare occurrences but can still have a huge impact on people. “I think that, the last 20 years, we’ve had one other occurrence of a burn crossing over from federal land onto private land in Oregon,” he said.
The Malheur National Forest supervisor notes that the spillover was quickly brought under control.
“They caught it with the resources they had on scene,” said Trulock. He noted that the number of crew on scene before the fire jumped was far more than their own burn plan had recommended, and that the new rules and added caution likely led to their ability to ultimately contain the spot. “We didn’t use any aviation or anything. The only additional resource we brought on was that dozer, and that was to really secure the edge of the spot so that they could then mop it up. So we were staffed enough to actually catch something like this.”
The Grant County Sheriff’s Office and the Forest Service estimated the size of the spot fire as approximately 20 acres. Chad Holliday estimates it as closer to 40, after measuring the perimeter of the area at “exactly one mile.”
‘Somebody’s got to be held accountable’
As the federal crews were attempting to control the spot fire on the ranch, McKinley arrived. Chad Holliday received a call from his sister, who was on the scene and told him to get home. He arrived to see Sheriff McKinley speaking with people along the fence.
“I walked up, and Todd said, ‘Chad, right now you’re (being) videorecorded. You’re the spokesman for the ranch. Would you like to press charges?’ And I said, ‘Absolutely. Somebody’s got to be held accountable.’”
Holliday said McKinley then went directly to Snodgrass on the county road and “put the cuffs on him.”
The Eagle has filed a public records request for bodycam footage or any other video taken at the scene during this incident by the Grant County Sheriff’s Office. The newspaper is also seeking any other video footage captured at the scene that could further help establish the sequence of events.
‘A reasonable person’
The fire was set in the days before predicted rain, and will likely prove to be the last of this year’s short burn season. But the issues surrounding prescribed burning and federal land management, especially as it impacts private landowners, will undoubtedly remain a flashpoint in Grant County.
For now, as the investigation continues, McKinley is playing things close to the vest. He’s declined offers to comment on the case beyond his initial press release, which said “details cannot be released at this time.”
Grant County District Attorney Jim Carpenter has been slightly more forthcoming, stating in his own press release that just because the burn boss was working as part of a federal crew doesn’t mean he will be shielded from potential legal consequences.
“To be clear, the employer and/or position of Snodgrass will not protect him if it is determined that he acted recklessly,” he wrote. “That the USFS was engaging in a prescribed burn may actually raise, rather than lower, the standard to which Snodgrass will be held.”
Carpenter lays out in his release the full legal standard for determining if a burn is or is not “reckless” as defined in Oregon statute: “The risk must be of such nature and degree that disregard thereof constitutes a gross deviation from the standard of care that a reasonable person would observe in the situation.”
McKinley, known as a level head in the wider context of Grant County politics, might not have intended to make a statement. But this extraordinary arrest has caught national attention and sparked debate in the press and online. And now in the actions of the sheriff and the actions of the Forest Service, both sides see actions that created real danger.
Critics of the Forest Service point to the simple fact that the fire escaped the lines as evidence the conditions were unsafe and that the fire should never have been approved. To the Hollidays, and those skeptical of federal land management in general, it’s a clear measure: the fire got onto their land and threatened or destroyed their property. How could that have been a reasonable thing to do?
It has also stirred the ire of wildland firefighter communities, who fear this development will set a precedent and only complicate an already difficult and dangerous job. And in these groups’ online conversations, it is clear many believe that the arrest created a situation on the ground that may have added to the real risk faced by fire crews in Bear Valley.
“One of the huge watch-out situations in any fire operation is a transition in leadership,” said Trulock. “And that’s when it’s a plan to transition in leadership. This was obviously unplanned. What I would say is there were definite heightened risks because of that action. Until leadership can be reestablished under a new person, then everybody is distracted because they know something happened. And so it created a huge distraction in the middle of what I would consider is a relatively high-risk operation.”
Adlam, the Extension Service fire specialist, agreed.
“The burn boss’s role is never more important than at the moment where something happens that is not part of the plan,” he said. “If you cut off the head of an operation before it’s finished, how is that supposed to be leading to a positive outcome?”
When reached for comment on this story, McKinley clarified why he’s reluctant to say too much at this point.
He said he knows how it appears in the court of public opinion to withhold detail, but added that as long as it protects the process he just doesn’t care. “I just want to respect the case and not get too much detail out so that it doesn’t mess with potential jury pools and all that,” he said, “because then we’d have to have (the trial) out of the area.”
For McKinley, the important thing is that the facts surrounding this case and the decisions of Rick Snodgrass are ultimately determined by 12 reasonable people — ideally, reasonable people from Grant County.
Blue Mountain Eagle reporter Tony Chiotti was on the scene of the Starr 6 prescribed burn before it jumped containment and spread to private land on Oct. 19. In reporting this story, he drew on observations made that day as well as multiple interviews with Forest Service officials, burn crew workers and landowners. If you have video footage from that day that can shed additional light on the sequence of events, please contact Chiotti at tchiotti@bluemountaineagle.com.